
kwoni's scavenger hunt 33 a diagram of a cell with structures
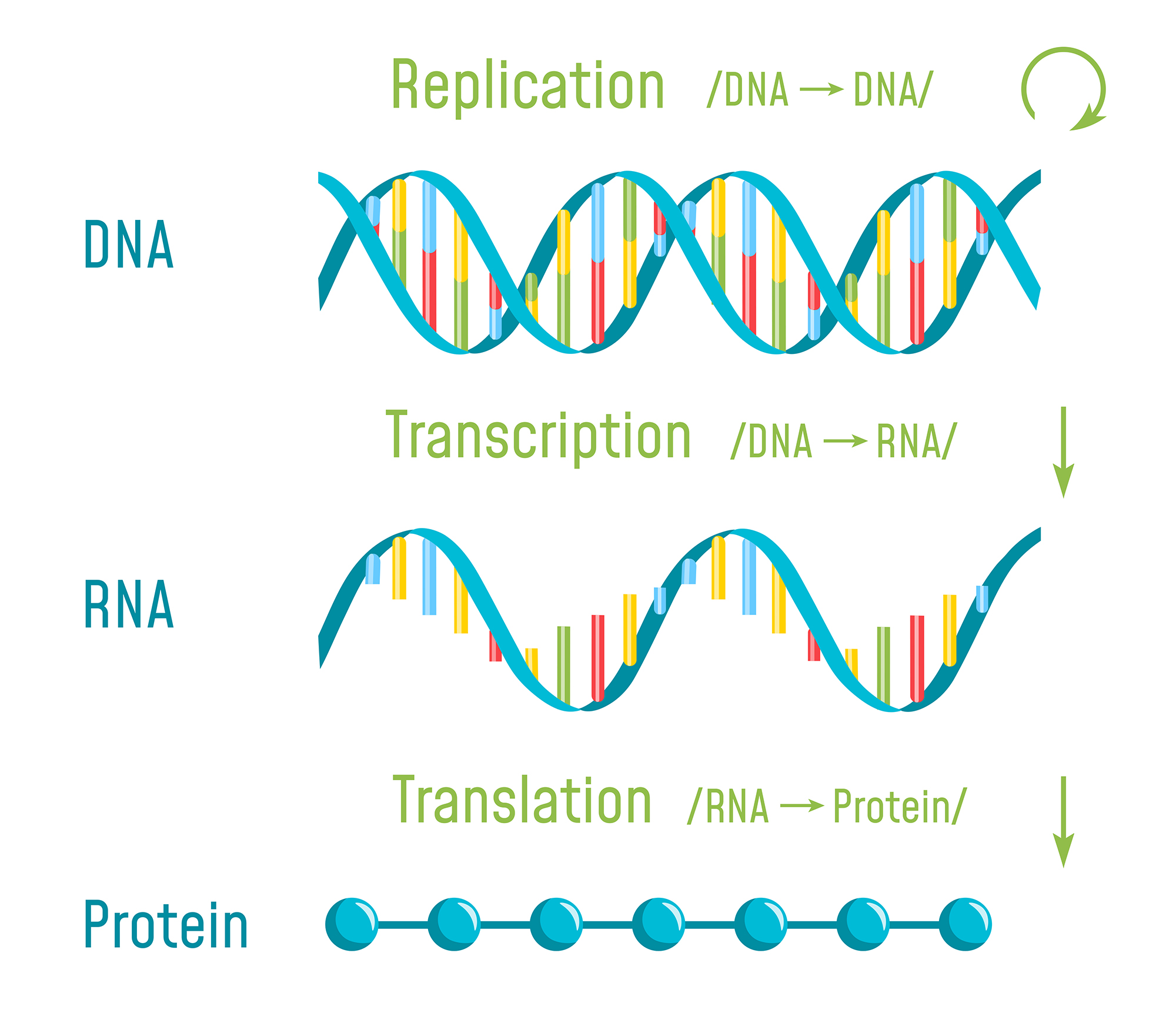
Meaning. RNA (ribonucleic acid) Single-stranded nucleic acid that carries out the instructions coded in DNA. Central dogma of biology. The process by which the information in genes flows into proteins: DNA → RNA → protein. Polypeptide. A chain of amino acids. Codon.
Protein Synthesis Nature Journals
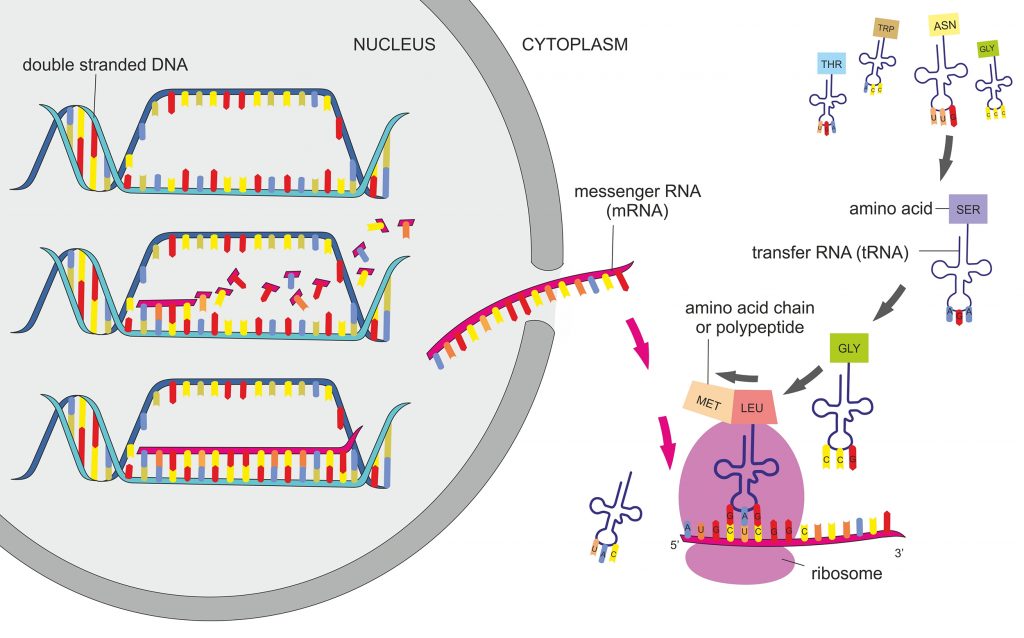
Protein synthesis consists of two main processes: transcription and translation. During the process of transcription —which occurs in the nucleus—an mRNA molecule is created by reading the DNA. Note that DNA never "becomes" RNA; rather, the DNA is "read" to make an RNA molecule. The mRNA leaves the nucleus and then, through the.
Protein Production A Simple Summary of Transcription and Translation
Protein Synthesis Labeled Diagram. 2) Translation: The Second Step of Protein Synthesis. Translation, the next major step of protein synthesis is the process in which the genetic code in mRNA is read to make the amino acids, which are linked together in a particular order based on the genetic code, forming protein.
Bio Geo Nerd Protein Synthesis
Here, we provide a description of the HILAQ method that includes procedures for (i) pulse-labeling and harvesting NSPs; (ii) addition of biotin by click reaction; (iii) protein precipitation;.

Diagram Of Protein Synthesis â Ready To Learn Biology Here We Go
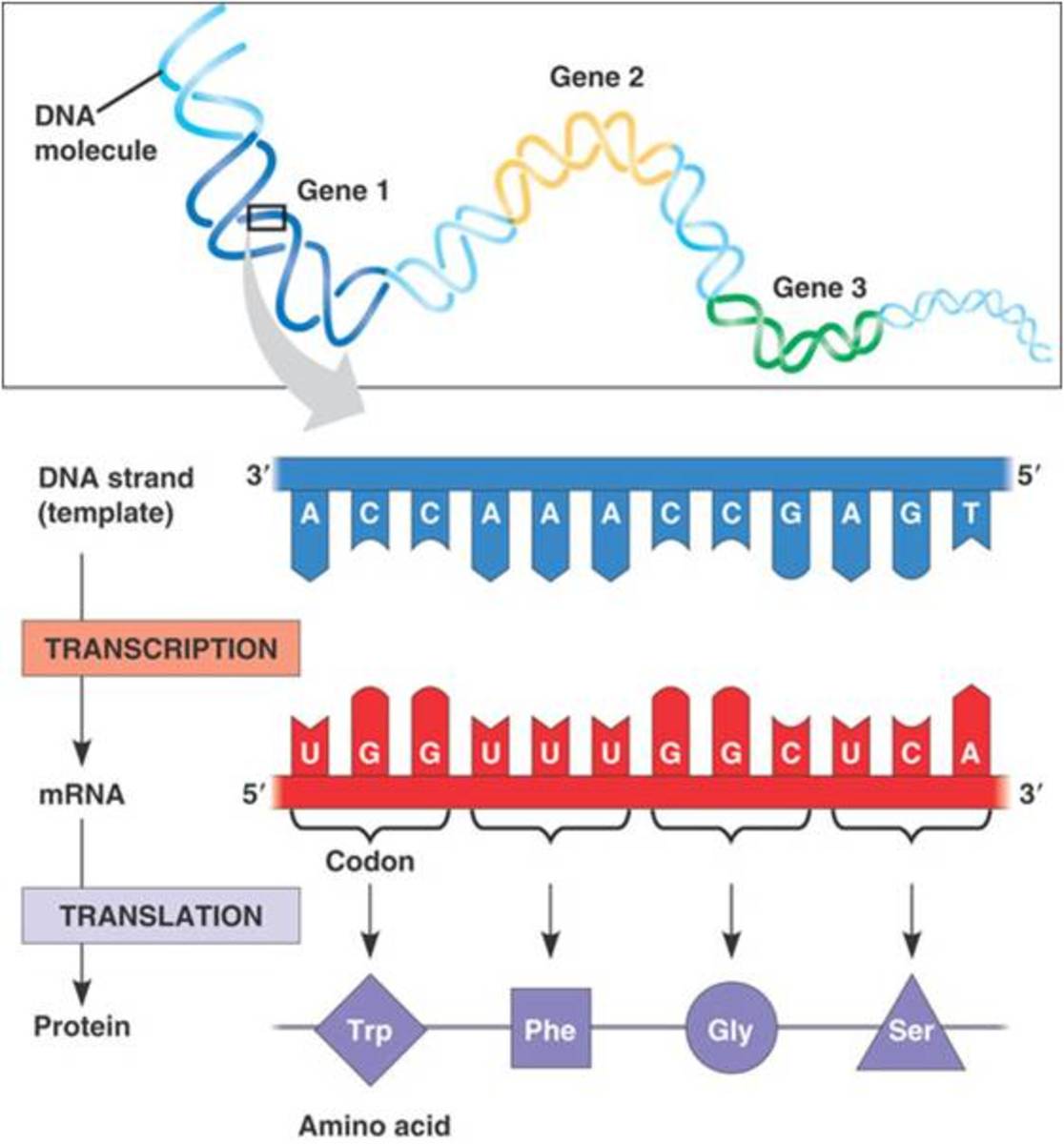
A specific transfer-RNA (tRNA) attaches to each specific amino acid and brings the amino acid to the RNA for incorporation. Figure 26.14. 1: Overview of protein synthesis. The first step in the process is transcription —the unfolding of DNA and the production of a messenger-RNA (mRNA) strand. This step takes place in the nucleus of the cell.

Protein Synthesis CK12 Foundation
Protein synthesis is process in which polypeptide chains are formed from coded combinations of single amino acids inside the cell. The synthesis of new polypeptides requires a coded sequence, enzymes, and messenger, ribosomal, and transfer ribonucleic acids (RNAs).
2b1 Protein Synthesis Nature Journals
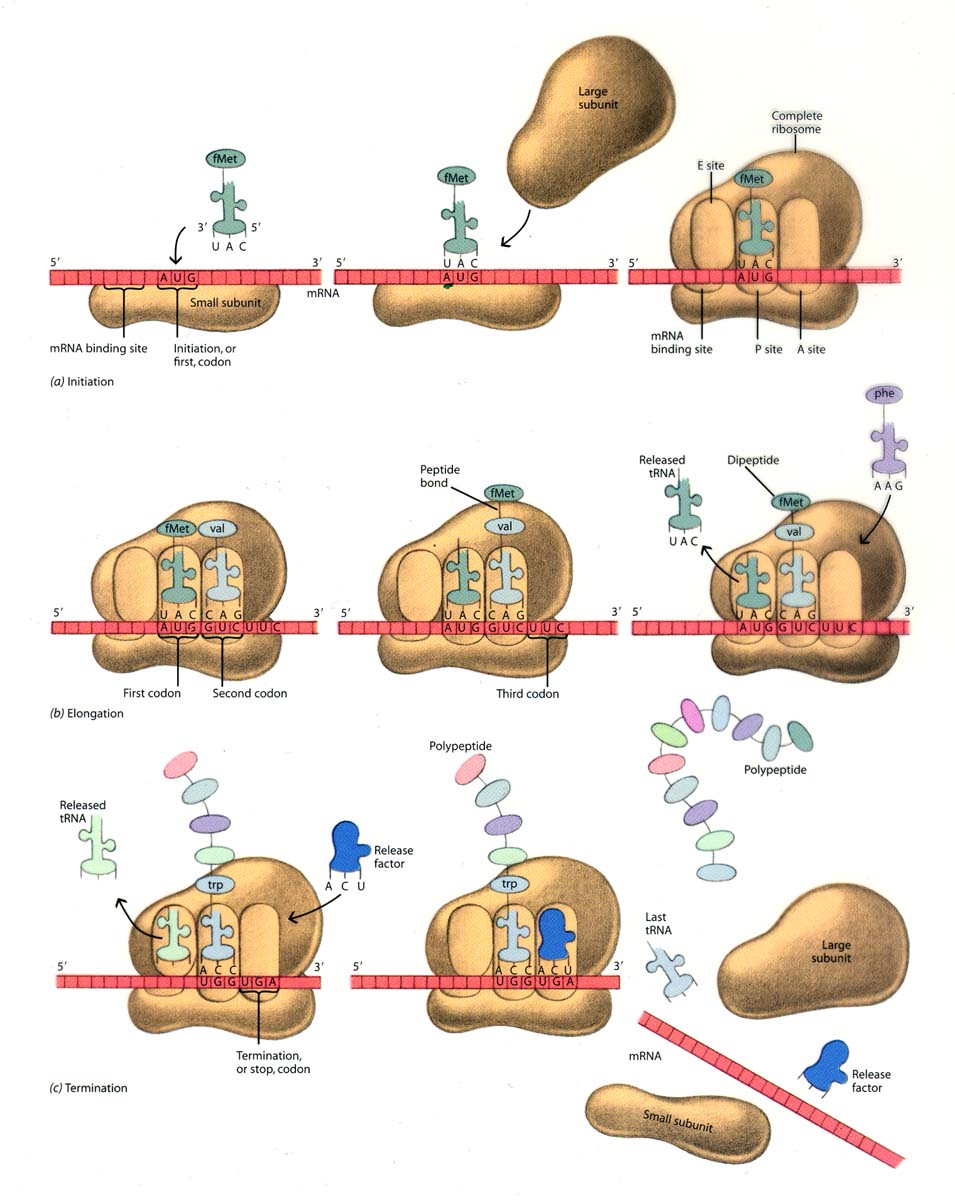
The translation is the second part of the central dogma of molecular biology: RNA --> Protein. It is the process in which the genetic code in mRNA is read to make a protein. The translation is illustrated in Figure 6.4.6 6.4. 6. After mRNA leaves the nucleus, it moves to a ribosome, which consists of rRNA and proteins.
WHAT IS PROTEIN SYNTHESIS ???? ALL ABOUT DNA AND RNA
Protein synthesis is a fundamental, tightly regulated cellular process, and several methods have been employed to measure the rate of protein synthesis in cells.. The amount of biotin-labeled.

Protein Synthesis MRS. MERRITT'S BIOLOGY CLASS
The nucleus. The nucleus (plural, nuclei) houses the cell's genetic material, or DNA, and is also the site of synthesis for ribosomes, the cellular machines that assemble proteins. Inside the nucleus, chromatin (DNA wrapped around proteins, described further below) is stored in a gel-like substance called nucleoplasm.
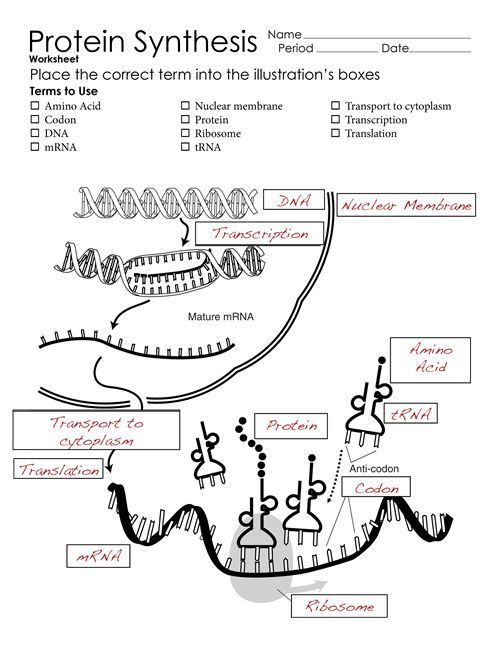
Protein Synthesis Diagram Worksheets
This is a demonstration of protein synthesis that will introduce you to the steps in making a polypeptide chain of amino acids. Key terminology is listed under the video. KEY TERMINOLOGY Nucleotide: a phosphate, sugar, and a base Codon: three nucleotides together, codes for a single amino acid
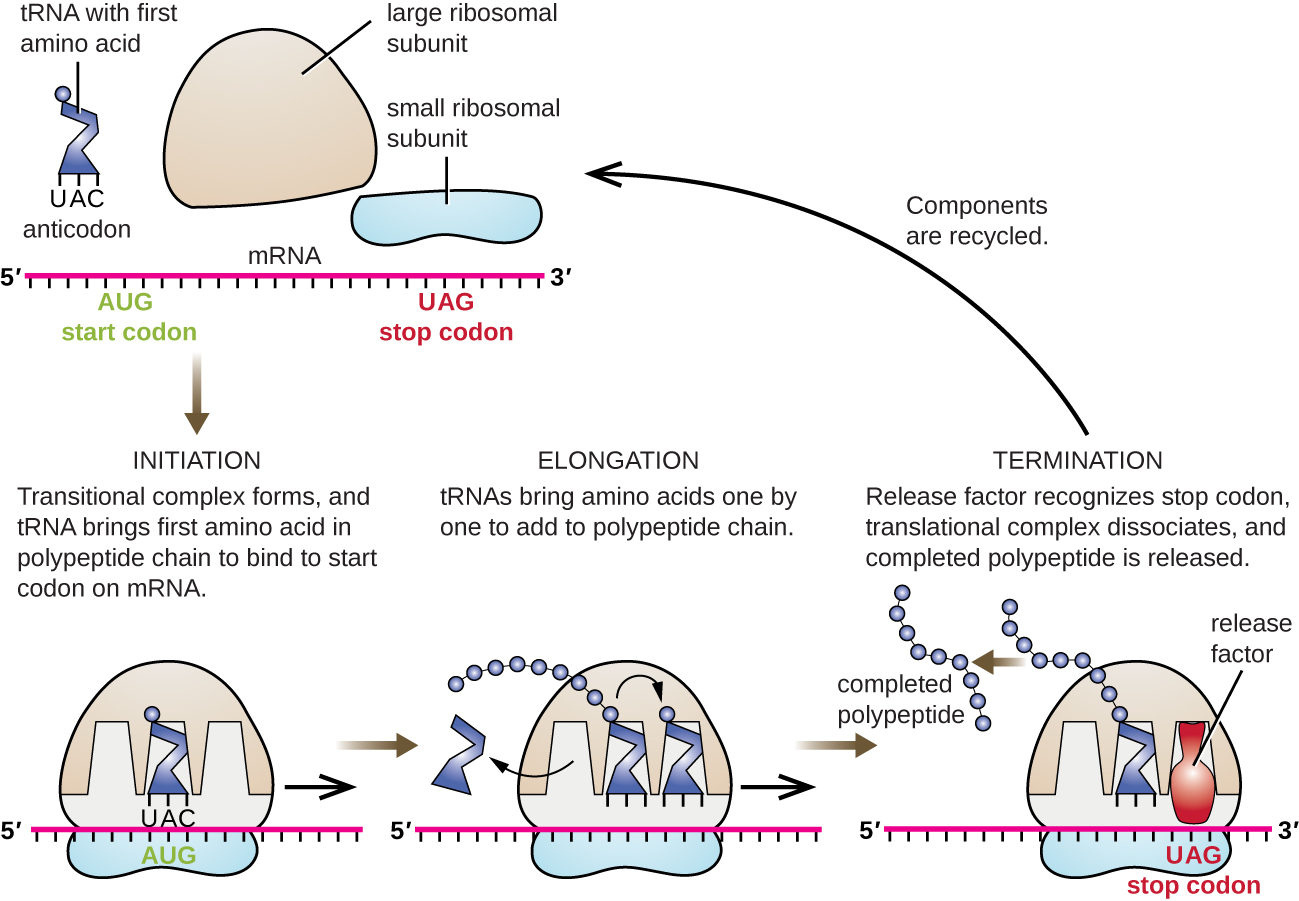
6.4 Protein Synthesis Biology LibreTexts
For FUNCAT analysis of protein synthesis 22,23,25,45, 8 h egg collections of OK371-GAL4 > UAS-MetRS L262G embryos were performed and animals were raised on Jazz-Mix Drosophila medium (Fisher.

Protein synthesis biological vector illustration scientific diagram
3.4 Protein Synthesis Learning Objectives Main Objective Explain the process by which a cell builds proteins using the DNA code By the end of this section, you will be able to: Explain how the genetic code within DNA determines the proteins formed Describe the process of transcription Explain the process of translation

Protein Synthesis
Fundamentals Protein synthesis involves a complex interplay of many macromolecules. Ribosomes: The eukaryotic ribosome has two subunits: a 40S small subunit and a 60S large subunit. Together, the eukaryotic ribosome is 80S.
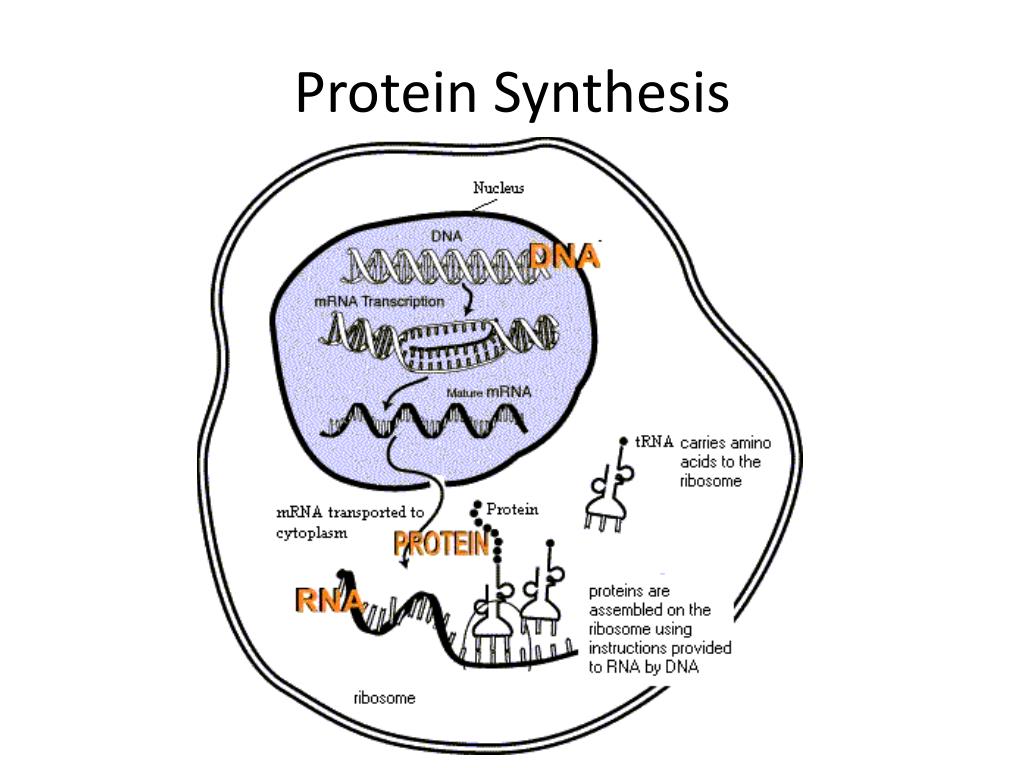
PPT Protein Synthesis PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1984857
Protein Synthesis and Degradation Assays Label nascent proteins, evaluate changes to protein expression, or study protein modification ‹ Cell Function Assays The independent mechanisms for the production and destruction of proteins, function together in the cell to maintain a balance, or homeostasis.
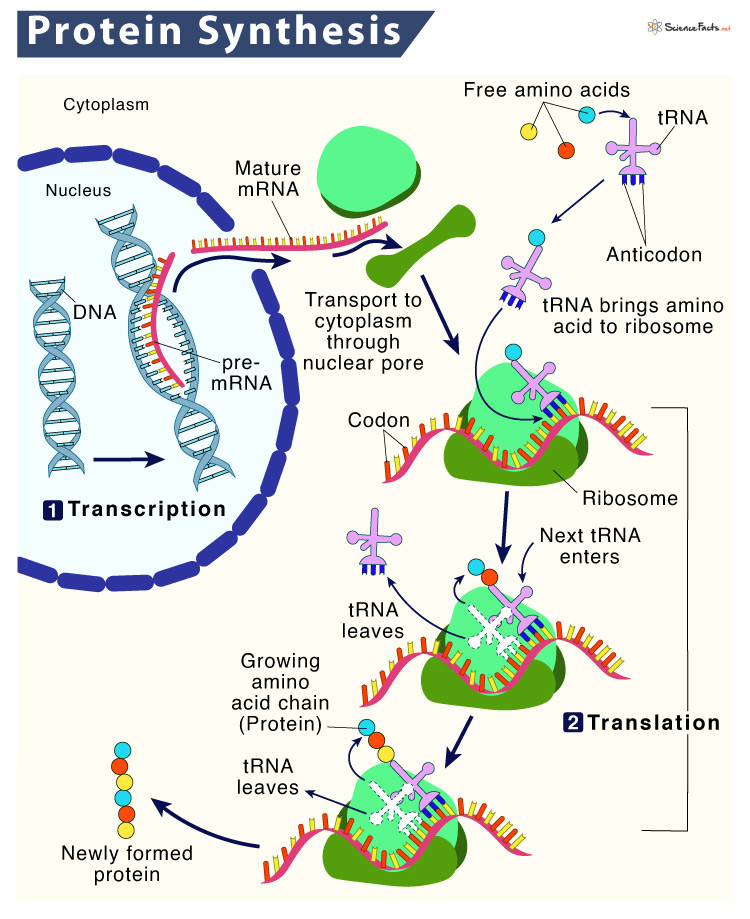
Protein Synthesis Location, Process, Steps, & Diagram
Amino acids. Amino acids are the monomers that make up proteins. Specifically, a protein is made up of one or more linear chains of amino acids, each of which is called a polypeptide. (We'll see where this name comes from a little further down the page.) There are 20 types of amino acids commonly found in proteins.
Fajarv Protein Synthesis Translation Diagram Labeled
Protein synthesis has long been thought of as a housekeeping process that is performed similarly by most cells. This is because traditional assays used to measure protein synthesis require.